Thursday, May 1, 2008
Sunday, April 27, 2008
CRCB-CHAPTER14 summy
In this chapter on evaluating internet resources, we will learn: how to use a seven-step evaluation system to determine the accuracy and reliability of internet information sources; how to use a rubric to rate website information.
Evaluating internet source of information helps we determine if they are reliable and useful. Knowing how to critically evaluate internet material not only helps we become a better student, but will help you in your work life beyond college.
Use the internet source evaluation system described in this chapter as a tool for assessing websites. Two Rand C A uses following seven steps:
1. know your purpose
2. double –check facts and sources
3. consider the source
4. evaluate content
5. determine intended audience
6. evaluate the writing
7. use what you already know.
Evaluating internet source of information helps we determine if they are reliable and useful. Knowing how to critically evaluate internet material not only helps we become a better student, but will help you in your work life beyond college.
Use the internet source evaluation system described in this chapter as a tool for assessing websites. Two Rand C A uses following seven steps:
1. know your purpose
2. double –check facts and sources
3. consider the source
4. evaluate content
5. determine intended audience
6. evaluate the writing
7. use what you already know.
CRCB-CHAPTER13 summy
In this chapter on critical reading comprehension, we will learn: what constitutes higher levels of thinking; how to use different lever of thinking to understand all type of reading material; how to create and answer questions based on we reading maternal in order to prepare for exams.
Critical reading comprehension involves challenging yourself to understand what we read in we book at different levers of complexity. Bloom’s taxonomy lists six lever of critical thinking ---knowledge, comprehension, application analysis, synthesis, and evaluation—that you can use to deepen we understanding of in the bookmaterial.
Critical reading comprehension involves challenging yourself to understand what we read in we book at different levers of complexity. Bloom’s taxonomy lists six lever of critical thinking ---knowledge, comprehension, application analysis, synthesis, and evaluation—that you can use to deepen we understanding of in the bookmaterial.
CRCB-CHAPTER12 Summary
Recognizing arguments as you read lets you critically examine an author’s line of reason and one conclusion. One way to detect them is to look for an author’s conclusions and then track the reasons he or she used to reach them. Another way is to look for the argument word clues an author used to indicate when reasons are being presented and conclusions stated.
When you find an argument, you should break it down into its constituent parts so that you can determine whether it is well found and logical.
Arguments can be evaluated using specific criteria including deterging dependability fact from opinion, and detecting fallacies.
The two primary types of arguments are deductive and inductive .Deductive arguments have at least one premise that logically leads to a conclusion. Inductive argument begging with a series of specific observation and conclude with a generalization that logically flow from them. As they are observation, even well-constructed inductive arguments cannot be considered absolutely true.Author’s view should be actively questioned so that flaws in the presentation of information are not passively accepted. Begging able to detect and evaluate argument in book, and to create argument using book reading material, forces to analyze the logic of what read and help we present we own ideas
In this chapter on argumentation ,we will learn: to identify arguments and their parts in book assignments; to dieting using between deductive and inductive arguments; to critically evaluate arguments in book and other reading media; to differentiate between fact and opinions; to understand and identify basic fallacies
When you find an argument, you should break it down into its constituent parts so that you can determine whether it is well found and logical.
Arguments can be evaluated using specific criteria including deterging dependability fact from opinion, and detecting fallacies.
The two primary types of arguments are deductive and inductive .Deductive arguments have at least one premise that logically leads to a conclusion. Inductive argument begging with a series of specific observation and conclude with a generalization that logically flow from them. As they are observation, even well-constructed inductive arguments cannot be considered absolutely true.Author’s view should be actively questioned so that flaws in the presentation of information are not passively accepted. Begging able to detect and evaluate argument in book, and to create argument using book reading material, forces to analyze the logic of what read and help we present we own ideas
In this chapter on argumentation ,we will learn: to identify arguments and their parts in book assignments; to dieting using between deductive and inductive arguments; to critically evaluate arguments in book and other reading media; to differentiate between fact and opinions; to understand and identify basic fallacies
Saturday, April 26, 2008
CRCB-CHAPTER 11 Summary
This chapter authors often use visual aids to help their readers better understand the information they are presenting. Visual information reinforces and supplements reading material. Types of visual aids include mind maps, outlines, charts, diagrams, graphs, illustrations, photographs, and time lines. The type of information being conveyed determines what type of visual aid an author will use. Learning how to read visuals will help understand and remember the textual information they illustrate.
An effective reading and study strategy is to make own visual aids. To create an effective visual aid, you have to recognize the important elements in what reading and be able to prioritize and organize them in a logical and useful format. It will quickly obvious how well know the material, you can’t draw a diagram or devise a table if you don’t understand what you have read or heard. In many instances, an effective visual will save from taking as many as many notes from notes from text or lectures.
In this chapter we will lean: to read visual information, such as charts, graphs, and photo; why authors select particular visuals to convey certain types of information to their readers. How to create visuals to help we remember information we have learned from we text.
An effective reading and study strategy is to make own visual aids. To create an effective visual aid, you have to recognize the important elements in what reading and be able to prioritize and organize them in a logical and useful format. It will quickly obvious how well know the material, you can’t draw a diagram or devise a table if you don’t understand what you have read or heard. In many instances, an effective visual will save from taking as many as many notes from notes from text or lectures.
In this chapter we will lean: to read visual information, such as charts, graphs, and photo; why authors select particular visuals to convey certain types of information to their readers. How to create visuals to help we remember information we have learned from we text.
CRCB-CHAPTER 9 Summary
The PSR technique requires that you question yourself before, during, and after you read. It encourage you to participate in reader-author conversation rather than to read passively
In this conversation, we can accrete author says and decide if it makes sense to we, we can also add what we know to the conversation by recalling related information. This cheaper helps we understand and remember the material, help we to understand the material on your own or alert we to the fact that we need to ask in a instructor for help.
The PSR technique also requires we to responds reading by writing in we journal. Commenting in writing helps we digest and understand an author’s ideas and articulate we own. By identifying exactly where we become confused in reading, we can return to that point and reread the relevant section of the text.
After reading this chapter ,we will know how to use the psr technique to better understand we textbooks; know how to create and answer preview questions ,and judge their effectiveness,; and we know to paraphrase ideas and summarize reading assignment.
In this conversation, we can accrete author says and decide if it makes sense to we, we can also add what we know to the conversation by recalling related information. This cheaper helps we understand and remember the material, help we to understand the material on your own or alert we to the fact that we need to ask in a instructor for help.
The PSR technique also requires we to responds reading by writing in we journal. Commenting in writing helps we digest and understand an author’s ideas and articulate we own. By identifying exactly where we become confused in reading, we can return to that point and reread the relevant section of the text.
After reading this chapter ,we will know how to use the psr technique to better understand we textbooks; know how to create and answer preview questions ,and judge their effectiveness,; and we know to paraphrase ideas and summarize reading assignment.
CRCB-CHAPTER 8 Summary
The authors usually organize information using certain classic methods or patterns.
Begging able to recognize organizational methods will help understand the ideas in how they are connected t each other, because they will fit into logical patterns already familiar with.
It will also help to remember what you have read, because you are not memorizing facts in isolation, but relating them to each other to form patterns that hold and organize them in your member. A useful way to identify an author’s method of organization is to look for the organization word clues that indicate which patterns using.
It is also important to assess an author’s overall method of organization. Author will frequently use more than one method from paragraph to paragraph to paragraph, but have one overall method for each.
And in this chapter we can will learn about different methods of textbook organization, learn to recognize that signal the different methods, practice techniques that will help we identify, organize and remember textbook methods of organization.
Begging able to recognize organizational methods will help understand the ideas in how they are connected t each other, because they will fit into logical patterns already familiar with.
It will also help to remember what you have read, because you are not memorizing facts in isolation, but relating them to each other to form patterns that hold and organize them in your member. A useful way to identify an author’s method of organization is to look for the organization word clues that indicate which patterns using.
It is also important to assess an author’s overall method of organization. Author will frequently use more than one method from paragraph to paragraph to paragraph, but have one overall method for each.
And in this chapter we can will learn about different methods of textbook organization, learn to recognize that signal the different methods, practice techniques that will help we identify, organize and remember textbook methods of organization.
Friday, April 25, 2008
Thursday, April 24, 2008
TFYChapter 12---deductive reasoning ---how do I reason from premises?
Chapter 12---deductive reasoning ---how do I reason from premises?
1. Deductive reasoning is the process of starting with one or more statements called premised and investing what conclusions necessarily follow from these premises.
2. Deduction is the subject of formal logic, whose main concern is with creating forms that demonstrate reasoning
3. Logic has its own technical vocabulary
4. The standardized language of syllogisms allows a reduction of everyday language into verbal equations.
5. Syllogisms allow logicians to determine what is being said, to identify hidden premises, and to find out if the argument makes sense.
6. Deductive and inductive reasoning are not isolated pursuits but are mentally interwoven both in major and mundane problem solving
7. It is possible to infer the rules of valid and invalid resigning from the study of models.
1. Deductive reasoning is the process of starting with one or more statements called premised and investing what conclusions necessarily follow from these premises.
2. Deduction is the subject of formal logic, whose main concern is with creating forms that demonstrate reasoning
3. Logic has its own technical vocabulary
4. The standardized language of syllogisms allows a reduction of everyday language into verbal equations.
5. Syllogisms allow logicians to determine what is being said, to identify hidden premises, and to find out if the argument makes sense.
6. Deductive and inductive reasoning are not isolated pursuits but are mentally interwoven both in major and mundane problem solving
7. It is possible to infer the rules of valid and invalid resigning from the study of models.
TFYChapter 11-inductive reasoning and inductive fallacies:How do I reason from evidence?
Chapter 11-inductive reasoning and inductive fallacies:
How do I reason from evidence?
1. Inductive reasoning is the process of thinking that you used in describing a fruit, vegetable, or tool in chapter
2. The inductive method is also called the empirical or scientific method
3. Induction arsons from evidence about some members of a class in order to form a conclusion about all members of that class.
4. Induction can be done through sensory observation, enumeration, analogous reasoning ,causal reasoning ,and pattern recognition
5. A hypothesis is a trial idea that can be used to further investigation in an inductive study
6. Inductive reasoning is used as a method for obtaining information when it would be impossible to examine all the data available
7. The five basic rules for evaluating the reliability of hypotheses based on statically samplings are as follow:
a. The greater the size of the sample, the greater is its probability of being representative of the whole of a population.
b. A sampling must be representative in order to lead to reliable results
c. One counterexample can refute a generalization arrived at through inductive reasoning
d. Statically evaluating should be offered in sufficient detail for verifications
e. When evaluating the results of polls, it is important to examine both the polling agency and polling question for bias.
How do I reason from evidence?
1. Inductive reasoning is the process of thinking that you used in describing a fruit, vegetable, or tool in chapter
2. The inductive method is also called the empirical or scientific method
3. Induction arsons from evidence about some members of a class in order to form a conclusion about all members of that class.
4. Induction can be done through sensory observation, enumeration, analogous reasoning ,causal reasoning ,and pattern recognition
5. A hypothesis is a trial idea that can be used to further investigation in an inductive study
6. Inductive reasoning is used as a method for obtaining information when it would be impossible to examine all the data available
7. The five basic rules for evaluating the reliability of hypotheses based on statically samplings are as follow:
a. The greater the size of the sample, the greater is its probability of being representative of the whole of a population.
b. A sampling must be representative in order to lead to reliable results
c. One counterexample can refute a generalization arrived at through inductive reasoning
d. Statically evaluating should be offered in sufficient detail for verifications
e. When evaluating the results of polls, it is important to examine both the polling agency and polling question for bias.
TFYChapter 10-fallacies: what’s a faulty argument?
Chapter 10-fallacies: what’s a faulty argument?
1. Word ambiguity uses undefined and vague words n an argument, seeking to gain an advantage by using words that could be interpreted in more than one way.
2. Misleading euphemisms are words that hide meaning by wrapping less acceptable ideas in positive or neutral connotations.
3. Prejudicial language persuades though the use of loaded words that convey a bias while pretending to convey objective information.
4. Appeals to fear and pity seek to persuade by affecting emotions rather than through sound rational support for an argument.
5. Appeal to false authority seeks to influences other by citing phony or inappropriate authorities
6. Appeal to bandwagon is another example of the appeal to authority
7. Personal attack refutes another argument by attacking the opponent rather than addressing the argument itself.
8. Poisoning the well seeks to prejudice other against a person, group, or idea and prevents their positions from being heard.
9. The red herring is a ploy of distraction
10. The straw man is an argument that misrepresents, oversimplifies, or caricatures an opponent’s position; it create a false replica, then destroys the replica.
11. Pointing to another wrong is also called two wrongs make a right.
12. Circular reasoning is the assertion or repeated assertion of a conclusion as though the conclusion were a reason.
1. Word ambiguity uses undefined and vague words n an argument, seeking to gain an advantage by using words that could be interpreted in more than one way.
2. Misleading euphemisms are words that hide meaning by wrapping less acceptable ideas in positive or neutral connotations.
3. Prejudicial language persuades though the use of loaded words that convey a bias while pretending to convey objective information.
4. Appeals to fear and pity seek to persuade by affecting emotions rather than through sound rational support for an argument.
5. Appeal to false authority seeks to influences other by citing phony or inappropriate authorities
6. Appeal to bandwagon is another example of the appeal to authority
7. Personal attack refutes another argument by attacking the opponent rather than addressing the argument itself.
8. Poisoning the well seeks to prejudice other against a person, group, or idea and prevents their positions from being heard.
9. The red herring is a ploy of distraction
10. The straw man is an argument that misrepresents, oversimplifies, or caricatures an opponent’s position; it create a false replica, then destroys the replica.
11. Pointing to another wrong is also called two wrongs make a right.
12. Circular reasoning is the assertion or repeated assertion of a conclusion as though the conclusion were a reason.
TFYChapter 9-----Argument summary
Chapter 9-----Argument summary
The critical reading of arguments is an active endeavor that requires involvement, interaction with questions, and evaluation.
The questions asked in the critical reading of arguments
The analysis of arguments in terms of their reasons and conclusions applies to both inductive arguments.
The conclusion of an argument is the last step in a reasoning process.
Reasons support conclusions
Arguments state and defend a claim in attempt to persuade.
Reports that only relate events or state facts cannot be analyzed as though they were arguments
An issue is a topic of controversy upon which positions many be taken. Surrounding each issue are many debate questions
The following questions can serve as guidelines for analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of arguments:
Are the reasons adequate to support the conclusion?
Are there any hidden assumption?
Are any central words ambiguous or slanted so as to incite prejudice?
Are there fallacies of reasoning?
Is any important information missing?
Is any information false or contradictory?
The critical reading of arguments is an active endeavor that requires involvement, interaction with questions, and evaluation.
The questions asked in the critical reading of arguments
The analysis of arguments in terms of their reasons and conclusions applies to both inductive arguments.
The conclusion of an argument is the last step in a reasoning process.
Reasons support conclusions
Arguments state and defend a claim in attempt to persuade.
Reports that only relate events or state facts cannot be analyzed as though they were arguments
An issue is a topic of controversy upon which positions many be taken. Surrounding each issue are many debate questions
The following questions can serve as guidelines for analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of arguments:
Are the reasons adequate to support the conclusion?
Are there any hidden assumption?
Are any central words ambiguous or slanted so as to incite prejudice?
Are there fallacies of reasoning?
Is any important information missing?
Is any information false or contradictory?
TFYChapter 8-----Viewpoints Summary
Chapter 8-----Viewpoints Summary
Critical thinking means learning to recognize viewpoints and how they shape the content of any message.
Viewpoints ---like assumptions, opinions, and evaluations—can be either conscious or unconscious.
We communicate best when we are aware of our own viewpoint and can understand and respect the viewpoints of other as well.
Writers shape their stories though their choice of a point of view; the choices include third-person, first-person, and multiple points of view.
Unconscious viewpoints include the egocentric, ethnocentric, and religiocentric.
Left, right, and centrist perspectives exit within both the Republican and Democratic parties.
The Internet provides a vehicle for the expression of a wide range of viewpoints not well represented in U S corporate media.
Periodicals can express viewpoints though images, words, and in the framing giving to information.
Critical thinking means learning to recognize viewpoints and how they shape the content of any message.
Viewpoints ---like assumptions, opinions, and evaluations—can be either conscious or unconscious.
We communicate best when we are aware of our own viewpoint and can understand and respect the viewpoints of other as well.
Writers shape their stories though their choice of a point of view; the choices include third-person, first-person, and multiple points of view.
Unconscious viewpoints include the egocentric, ethnocentric, and religiocentric.
Left, right, and centrist perspectives exit within both the Republican and Democratic parties.
The Internet provides a vehicle for the expression of a wide range of viewpoints not well represented in U S corporate media.
Periodicals can express viewpoints though images, words, and in the framing giving to information.
Wednesday, April 2, 2008
Tuesday, April 1, 2008
Monday, March 31, 2008
TFY-CHAPTER 7 Summary
1.Evaluations make judgments about worth on the basis of standards that may be conscious or unconscious.
2.Evaluations can help us react quickly to situationd in which our survival is at stake .
3.Evaluations are not facts.
4.Premature evaluations are hasty evaluations that contain unexamined or faulty support.
5.Feelings and expectations affect both our perceptions and our evaluations.
6.All of us need to learn how to make fair and sound evaluations because they affect our livers constantly.
7.Connotative words convey evaluations that can be used to sway our opinions.
8.Evaluations are used in advertising and journalism to persuade us, sometimes hynotically ,to make positive associations with products and purchase them.
9.Critical thinking requires that we stay alert to manipulative advertising techniques that are most effective when we can be enticed to enter into a trance state.
10.Propaganda used manys sophisticated manipulative techniques of persuasion.
2.Evaluations can help us react quickly to situationd in which our survival is at stake .
3.Evaluations are not facts.
4.Premature evaluations are hasty evaluations that contain unexamined or faulty support.
5.Feelings and expectations affect both our perceptions and our evaluations.
6.All of us need to learn how to make fair and sound evaluations because they affect our livers constantly.
7.Connotative words convey evaluations that can be used to sway our opinions.
8.Evaluations are used in advertising and journalism to persuade us, sometimes hynotically ,to make positive associations with products and purchase them.
9.Critical thinking requires that we stay alert to manipulative advertising techniques that are most effective when we can be enticed to enter into a trance state.
10.Propaganda used manys sophisticated manipulative techniques of persuasion.
TFY-CHAPTER 6 Summary
1.Although the word opinion is a common one ,it is just as commonly misunderstood
2.Opinions can be well substantiated or not
3.Critical thinking requires that we recognize the difference between reponsible and irresponsible opinion and that we distinguish statements based on evidence form statements based solely on feelings
4.People enjoy expressing and reading opinions.
5.Expert opinion is based on an understanding of evidence and risks in a situation and is important and highly valued.
6.Public opinion polls can be used to determine pubilc sentiment on social and po;itical issues but also to manipulate public sentiment.
7.opinions should not be confused with facts.
8.Arguments consist of supported opinions;the internt of an argument is to persuade.
9.In an essay, a statement of opinion can be the thesis or its principal claim.
2.Opinions can be well substantiated or not
3.Critical thinking requires that we recognize the difference between reponsible and irresponsible opinion and that we distinguish statements based on evidence form statements based solely on feelings
4.People enjoy expressing and reading opinions.
5.Expert opinion is based on an understanding of evidence and risks in a situation and is important and highly valued.
6.Public opinion polls can be used to determine pubilc sentiment on social and po;itical issues but also to manipulate public sentiment.
7.opinions should not be confused with facts.
8.Arguments consist of supported opinions;the internt of an argument is to persuade.
9.In an essay, a statement of opinion can be the thesis or its principal claim.
TFY-CHAPTER 5 Summary
1.An assumption is something we take for granted somthing we accept prematurely is ture.
2.Assumptions can be conscious or unconscious,warranted or unwarranted.
3.Hidden assumptions are unconscious assumptions that greatly influence a line of reasoning .
4.Arguments are the use of reasoning to defend an idea or to persuade someone else to believe in the idea .
5.We perceive incongruities when observe situations that do not meet our expectations or assumptions.
6.Bring fresh perspective to a problem that has stumped other is ofern able to find a solution
2.Assumptions can be conscious or unconscious,warranted or unwarranted.
3.Hidden assumptions are unconscious assumptions that greatly influence a line of reasoning .
4.Arguments are the use of reasoning to defend an idea or to persuade someone else to believe in the idea .
5.We perceive incongruities when observe situations that do not meet our expectations or assumptions.
6.Bring fresh perspective to a problem that has stumped other is ofern able to find a solution
Sunday, March 30, 2008
TFY-CHAPTER 4 Summary
1.The word infer means:
A.Derive by reasoning;
B. Conclude;
C.Guess
2.Responsible report writing or desciptive writing lets the facts speak for themselves as much as possible.
3.Writing that offers spcific detailed support for its conclusions makes interesting writing .
4.reasonable inferences can be used in descriptive writing to tie facts together.
5.In solving problems,inferences can be use as a strategy in planning and choosing altematives.
6.Detectives and consultants of all kinds are valued for their ability to examine facts and make the best inferences from them.
7.Inference tend to build on inferences in chains of associaition
8.Facts and inferences are linked together through generalizations.
9.The topic sentence of a paragraph is a generaliztion that summarize the main idea to be demonstred in that paragraph.
A.Derive by reasoning;
B. Conclude;
C.Guess
2.Responsible report writing or desciptive writing lets the facts speak for themselves as much as possible.
3.Writing that offers spcific detailed support for its conclusions makes interesting writing .
4.reasonable inferences can be used in descriptive writing to tie facts together.
5.In solving problems,inferences can be use as a strategy in planning and choosing altematives.
6.Detectives and consultants of all kinds are valued for their ability to examine facts and make the best inferences from them.
7.Inference tend to build on inferences in chains of associaition
8.Facts and inferences are linked together through generalizations.
9.The topic sentence of a paragraph is a generaliztion that summarize the main idea to be demonstred in that paragraph.
TFY-CHAPTER 3 Summary
1.By definition ,a fact is something know with certainty through experience,observation,or measurement.
2.It is not easy for us to determine whether facts correspond to reality.
3.The difference between fact and fiction does matter
4.Feelings are facts
5.Facts are not absolutes but statemnts of probility.
6.lead us to distrust or distort our own perceptions.
7.Our senses are limited both in range and capcity and affected by many factors,such as selective fous and mental preocupations.
8.Following characteristics:
A.Define own limitations.
B.Objectively stated.
C.Use appropritate qualifiers.
D.State the obvious.
E.Not inappropiately cautious.
F.Not include guesses of inferences.
G.Specific and offer their evidence for others to verify.
9.Use to determine facts are verifiability,reliability,probability,and plausibility.
2.It is not easy for us to determine whether facts correspond to reality.
3.The difference between fact and fiction does matter
4.Feelings are facts
5.Facts are not absolutes but statemnts of probility.
6.lead us to distrust or distort our own perceptions.
7.Our senses are limited both in range and capcity and affected by many factors,such as selective fous and mental preocupations.
8.Following characteristics:
A.Define own limitations.
B.Objectively stated.
C.Use appropritate qualifiers.
D.State the obvious.
E.Not inappropiately cautious.
F.Not include guesses of inferences.
G.Specific and offer their evidence for others to verify.
9.Use to determine facts are verifiability,reliability,probability,and plausibility.
TFY-CHAPTER 2 Summary
1.An accurate use of words improves our thinking.
2.Writing helps us learn more about words and how to use them.
3.Clears thinking depends on a clear understanding of the words we use.
4.We need to understand what dictionaries can and cannot offer us;we need to use them skillfuly and frequently.
5.The thesaurus helps us when we are writing and translating noverbal experience and ideas into words ;the dictionary helps us when we are reading and interpreting the words of ofthers.
6.Defintions set boundaries for word ideas and show us their specfic and general characteristics and how they are relateed to or distinguished from one another.
7.Dictionary definition show us the agreements that society has made about a word's meaning.
8.The test our understanding of aword is our ability to define it.
9.A study of a word's etymology can help us trace a word back to its earliest root idea and can give us an image that convey a more concretesense of the word's logic.
10.The connotation of a word are its associative meanings, whic can be positive,negative,or thoughts.
11.The first stage of critical eading is objective receptivity to the material;this means having the technical ability as well as the willingness to accurately reproduce its content without alterations or distortions .
Instruction for assignment
Step1:suppose you choose as your topic defining adult
Step2:try clustering with the word adult
Step3:take information you discoverd form your cluster and begin to write a good paragraph about the various meaning and boundaries of the word adult.
2.Writing helps us learn more about words and how to use them.
3.Clears thinking depends on a clear understanding of the words we use.
4.We need to understand what dictionaries can and cannot offer us;we need to use them skillfuly and frequently.
5.The thesaurus helps us when we are writing and translating noverbal experience and ideas into words ;the dictionary helps us when we are reading and interpreting the words of ofthers.
6.Defintions set boundaries for word ideas and show us their specfic and general characteristics and how they are relateed to or distinguished from one another.
7.Dictionary definition show us the agreements that society has made about a word's meaning.
8.The test our understanding of aword is our ability to define it.
9.A study of a word's etymology can help us trace a word back to its earliest root idea and can give us an image that convey a more concretesense of the word's logic.
10.The connotation of a word are its associative meanings, whic can be positive,negative,or thoughts.
11.The first stage of critical eading is objective receptivity to the material;this means having the technical ability as well as the willingness to accurately reproduce its content without alterations or distortions .
Instruction for assignment
Step1:suppose you choose as your topic defining adult
Step2:try clustering with the word adult
Step3:take information you discoverd form your cluster and begin to write a good paragraph about the various meaning and boundaries of the word adult.
Saturday, March 29, 2008
TFY-CHAPTER 1 Summary and QUIZ
1.First observe our own thinking processes so we can recognize our strengths and weaknesses.
2.Help us see details and new knowledge.
3.observation is process of sensing ,perceiving ,and thinking .
4.Requirese to stay awake,take our time ,give full attention ,and suspend thinking in an attitude of listening .
5.Skills are self-understanding ,creativty,rapture,power ,and wonde.
TFY--CHAPTER 1 QUIZ P39
1.Observation skills are learned mainly through book learing.support for answer:on the contrary,observation is leaned form participation,which is more active and spontanecous than reading.samuel scudder learned observing though the active coaching of his teacher agassiz as well as from his own efforts, curiosity,and persistence in studying his fish.-------false 2.the standard academic study of all the physical sciences requires observation skills,whether in the field or laboratory----ture 3.in thinking,the correctness of our conclusions usually depends on the clearity of our perceptions.----false 4.observation skills can be extended to observing how you observe.-----ture 5.an insight is an experience of understanding that can occur spontaneously affter we observe something intently for a while.one illustration of this experience is the story of archimedes,who,while in his bath,discovered the means of meaning the volume of an irregular solid by the displacement of water.---false 6.agassiz was simply too busy to give his student all the assistance he needed.----ture 7.perception and sensation are synonyms.---ture 8.it is difficult to feel sensation and to think at the same time.if we want to feel whether a pair of new shose fits properly,we have to pay attention----ture 9.assimilation,according to piaget,is an experience of easily understanding something that reading fits into our preexisting schemes or worldview.---false 10.the word thinking,according to the dictionary,has only one meaing .----ture
2.Help us see details and new knowledge.
3.observation is process of sensing ,perceiving ,and thinking .
4.Requirese to stay awake,take our time ,give full attention ,and suspend thinking in an attitude of listening .
5.Skills are self-understanding ,creativty,rapture,power ,and wonde.
TFY--CHAPTER 1 QUIZ P39
1.Observation skills are learned mainly through book learing.support for answer:on the contrary,observation is leaned form participation,which is more active and spontanecous than reading.samuel scudder learned observing though the active coaching of his teacher agassiz as well as from his own efforts, curiosity,and persistence in studying his fish.-------false 2.the standard academic study of all the physical sciences requires observation skills,whether in the field or laboratory----ture 3.in thinking,the correctness of our conclusions usually depends on the clearity of our perceptions.----false 4.observation skills can be extended to observing how you observe.-----ture 5.an insight is an experience of understanding that can occur spontaneously affter we observe something intently for a while.one illustration of this experience is the story of archimedes,who,while in his bath,discovered the means of meaning the volume of an irregular solid by the displacement of water.---false 6.agassiz was simply too busy to give his student all the assistance he needed.----ture 7.perception and sensation are synonyms.---ture 8.it is difficult to feel sensation and to think at the same time.if we want to feel whether a pair of new shose fits properly,we have to pay attention----ture 9.assimilation,according to piaget,is an experience of easily understanding something that reading fits into our preexisting schemes or worldview.---false 10.the word thinking,according to the dictionary,has only one meaing .----ture
Friday, March 28, 2008
CRCB-CHAPTER 7 Summary
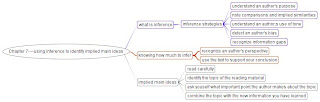
College instructors require you not only to read and understand what is explicitly stoned on the page, but also to detect ideas that are implied or indirectly stated. In order to fully understand a reading assignment, you need to reading assignment ,we can read the material and combine what is stated with the additional information generate using infence as a tool.
In this chapter on advanced reading comprehension, we can learn:
What inference is ?
Strategies you can use to infer an author's meening as you read.
What limits the amount of information you should inter.
How to identify implied main ideas.
In this chapter on advanced reading comprehension, we can learn:
What inference is ?
Strategies you can use to infer an author's meening as you read.
What limits the amount of information you should inter.
How to identify implied main ideas.
CRCB-CHAPTER 6 Summary
Authors use details to help readers understand their ideas and arguments.Details are specific pieces of information that server as the "arms and legs" of the main idea.They are usually presented as facts,opinions,examples,illustration, explanations or definited and are frequently discovered by asking question such as who,what , when,how or why.About the main idea.Major details provide support to the main idea in a reading .Minor details clarify major details.
In this chapter you will learn:
What supporting details are.
How to distinguish between details and main ideas.
How to identify and prioritize majoy and minor details in paragraphs,articles,and texbook chapters
In this chapter you will learn:
What supporting details are.
How to distinguish between details and main ideas.
How to identify and prioritize majoy and minor details in paragraphs,articles,and texbook chapters
CRCB-CHAPTER 5 Summary
The ablity to locate an author's main idea is key to understanding your reading.In order to see the relationship between the main idea and the details that support it ,you must first distinguish between general ideas and more specific ones.The topic is the most general idea.The main idea is the more specific controlling idea of a piece of writing .The details ,which are the most specific,support and illustrate the main idea.
In the chapter we can lean:
What main ideas are .
Srategies for identifying main ideas in paragrphs and longer reading
How to cleck whether you have correctly identified main ideas
In the chapter we can lean:
What main ideas are .
Srategies for identifying main ideas in paragrphs and longer reading
How to cleck whether you have correctly identified main ideas
CRCB-CHAPTER 4 Summary
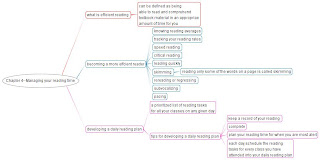
After reading this chapter we can know:
What efficient reading is ?
How to track your reading rate and compute you’re reading rate averages in different subjects
How to develop a daily reading plan
Several strategies, including skimming, regressing, subvocailizing, and pacing, that will increase your reading efficiency.
Comprehension should be your main reading goal, not how fast you read.
Develop a general study schedule that shows specifically when you plan to study for each class and for how long.
The reading tips suggested in this chapter that will contribute to your becoming a more efficient reader are: reading quickly when appropriate, skimming, regressing or rereading, subvocalizing, pacing.
What efficient reading is ?
How to track your reading rate and compute you’re reading rate averages in different subjects
How to develop a daily reading plan
Several strategies, including skimming, regressing, subvocailizing, and pacing, that will increase your reading efficiency.
Comprehension should be your main reading goal, not how fast you read.
Develop a general study schedule that shows specifically when you plan to study for each class and for how long.
The reading tips suggested in this chapter that will contribute to your becoming a more efficient reader are: reading quickly when appropriate, skimming, regressing or rereading, subvocalizing, pacing.
CRCB-CHAPTER 3 Summary
Memory is the process of storing and retrieving information. You will have difficulty remembering what you read if you do not know the stages in the memory process, and purposely use strategies at each stage to ensure that newly learned information become permanently stored.
The three primary stages in the memory process are sensory member, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Specific strategies you can use to enhance your sensory memory include the following :reading your text aloud, drawing pictures of the information you are leaning ,acting out a chapter in front of a mirror or an audience ,visualizing information in your head, using your fingers to point to new words ,and reading while riding an exercise bike. Chunking is an effective strategy for organizing and remembering new information so that t remains in your short-term memory long enough to transfer into your long-term memory.
In this chapter we can learn:
1. The three stages of the memory process and how they work
2. Strategies to help you process information at each stage of the memory process
3. Why you can forget what you read or hear
The three primary stages in the memory process are sensory member, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Specific strategies you can use to enhance your sensory memory include the following :reading your text aloud, drawing pictures of the information you are leaning ,acting out a chapter in front of a mirror or an audience ,visualizing information in your head, using your fingers to point to new words ,and reading while riding an exercise bike. Chunking is an effective strategy for organizing and remembering new information so that t remains in your short-term memory long enough to transfer into your long-term memory.
In this chapter we can learn:
1. The three stages of the memory process and how they work
2. Strategies to help you process information at each stage of the memory process
3. Why you can forget what you read or hear
CRCB-CHAPTER 2 Summary
Vocabulary building is one of the most important reading strategies you can learn. By increasing your vocabulary, you increase you understanding of textbook information. You also increase you ability to speak and write well-to communicate effectively. A rich vocabulary allow you access to many types of reading material, while limited one prevents you from fully understanding what you read.
Although no one knows every word, or interrupts reading to look up every unfamiliar word in the dictionary, using the simple strategies presented will help you figure out and remember the meaning of new words.
An important way to make new words a part of your regular vocabulary is to use them in your everyday speech and writing in your journal daily will help!
in this chapter we'll learn:
1-why developing you vocabulary is important
2-how to discover the ,meaning of a word using context clues and word analysis
3-how to remember new vocabulary words using word maps,the card review system,and journal writing
4-what test-talking vocabulary means
Although no one knows every word, or interrupts reading to look up every unfamiliar word in the dictionary, using the simple strategies presented will help you figure out and remember the meaning of new words.
An important way to make new words a part of your regular vocabulary is to use them in your everyday speech and writing in your journal daily will help!
in this chapter we'll learn:
1-why developing you vocabulary is important
2-how to discover the ,meaning of a word using context clues and word analysis
3-how to remember new vocabulary words using word maps,the card review system,and journal writing
4-what test-talking vocabulary means
CRCB-CHAPTER 1 Summary
Reading is an active process based on an active process besides on author’s to convey meaning though the write word and your ability to extract meaning from those words. Keeping a learning journal is also an active learning task. It helps you identify what you understand in a reading assignment and what is still unclear. It can help you to understand how you learn, which learning styles work best for you, and how you can improve those with which you have difficulty. Using learning will help you to identify, analyze and correct reading and leaning difficulties.
In this chapter we'll learn:
What reading is?
How effective journaling helps you read better
What concentration is?
What is involved in active reading and learning
Techniques for improving your concentration while reading
In this chapter we'll learn:
What reading is?
How effective journaling helps you read better
What concentration is?
What is involved in active reading and learning
Techniques for improving your concentration while reading
Thursday, March 27, 2008
Wednesday, March 26, 2008
Tuesday, March 25, 2008
Thursday, February 14, 2008
Where do you stand?
 Where do you stand?
Where do you stand?Sometime, we stand in there, you will asks yourself, where are you? When you have a problem, you will ask yourself: how do I do? You will think, so what is critical thinking?
Open we book, we can saw: critical thinking---brings conscious awareness, skills, and standards to the process of observing, analyzing, reasoning, evaluating, reading, and communicating. Let me continue:
FEET: What do I stand for as a foundation of critical thinking?
I stand for as a foundation of critical thinking, I will ask myself: why we learn critical thinking? We know many complex kinds of thing, for many purposes. Critical thinking has its basis in intellectual criteria that go beyond subject-matter divisions and which include: clarity, credibility, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, significance and fairness. So, we need a lot of knowledge on important topics for critical thinking.
STOMACH: What upsets me about critical thinking?
On mine growth road, I will get a problem, life will took you how to do next step! But you has own mind, your friend, your family they will give the instruction for your, on that time, you can use critical thinking to chose your way. Critical think help your find the better.
HEART: What do I love about critical thinking?
I love critical thinking, it helps me exercise more awareness and self-control, help me make better decisions, help me……
HANDS: What do I feel about critical thinking?
It can help you got skill for critical thinking, critical thinking isn’t the only from of clear thinking, nor is it always appropriate. Uses writing to improve thinking and got ideas across.
EARS: What do I hear about critical thinking?
We can leistering the new, a radio……to lean more skill for critical thinking, helpful we’re choose and observes.
EYES: What do I see about critical thinking?
Reads critically and observes, got the ideas across to have own mind to lessening the likelihood of making serious mistakes.
BRAIN: What do I think about critical thinking?
Critical thinkers gather information from all senses, verbal and written expressions, reflection, observation, experience and reasoning. Got the habits of critical thinking, it is helpful you to do anything.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





+stratgies.png)